Millennial Vaccination Habits Vary by Ethnicity
But opinions about early childhood and HPV vaccines contradict. Why the difference?
Whenever there is an outbreak of the measles, mumps or some other vaccine preventable infectious disease, we hear a lot about herd immunity - the notion that if 90%-95% of a population is vaccinated infectious diseases cannot get a toehold in a population. This idea, however, may be providing us a false sense of security because for herd immunity to work, vaccinated individuals need to be distributed evenly among a population to act as buffers against transmission and, it turns out, they’re not.
Earlier this year, we ran a nationally representative survey among 570 adults with kids and asked them about their children’s vaccinations. As a whole, the results are not great but acceptable. 85% of parents either did or intend to vaccinate their children according to recommended schedules with another 10% vaccinating but on a longer, though not recommended, schedule. Based on this, we might take comfort in the knowledge that 90% to 95% of kids will be fully vaccinated by the time they start school.
Age and Ethnicity Matter
But will that be the case in your child’s school? That depends on who your neighbors are. It turns out there are large differences in vaccination habits driven by age and ethnicity. 91% of Gen X parents either did or intend to vaccinate according to the recommended schedules while only 78% of Millennial parents are on board with this approach. Adding in the 15% of Millennial parents who plan to vaccinate on a longer schedule brings us to more acceptable 93% but uncertainty remains as to the herd immunity of younger age groups.
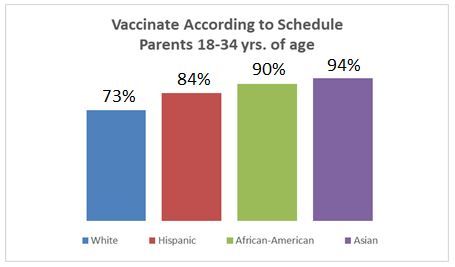
When combining age and ethnicity, the difference in early childhood vaccination rates becomes even more stark.
When adding in those parents who chose to vaccinate on longer schedules all ethnic groups climb above 90% though White Millennials still have the highest rate of parents who say they won’t vaccinate at all at 6% and Hispanics the lowest at 3%.
HPV Vaccine is an Exception
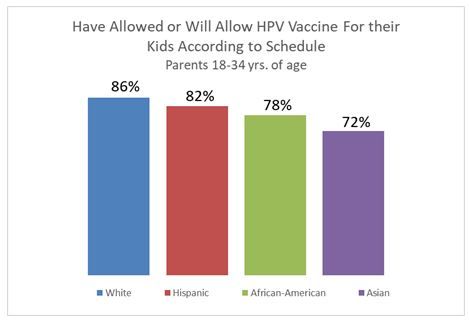
Why aren’t these parents vaccinating their young kids according to schedule? The most common answer is “I don’t think it’s necessary to immunize” followed by “I don’t think immunizations are effective.” Fears of autism, fortunately, are starting to wane as this reason did not even break the top five. White Millennial Parents, however, appear to have a change of heart when it comes to the HPV vaccine which is generally given at around ages 11 and 12. Here they’re ahead of the curve.
Why the change? What happens between the ages of 2 and 11 that makes White Millennial parents decide vaccinating is OK and Asian and African American parents start to question its merits? Unlike the early childhood vaccines which are considered unnecessary or ineffective by the abstainers, the #1 reason given for not letting their kids get the HPV vaccine is that it “Makes them sick.” Where are parents getting the idea from? The internet may be one reason. Currently, the #4 organic search result on Google after the CDC website and a couple other pro-vaccine sites for the search “Is the HPV vaccine safe?” is an article entitled “It’s official: HPV vaccine, the most dangerous vaccine yet” published on anhinternational.org (Alliance for Natural Health).
Google search results, however, can’t be the sole reason we’re seeing differences by ethnicity since negative articles about early childhood vaccines are also prevalent and the vaccination likelihood trend by ethnicity is reversed for the HPV vaccine. The answer? Well, the base sizes we’re dealing with here are small and further research is needed but directionally it looks like the answer may be attitudes towards sex. Among parents that said they have not or would not allow their kids to receive the HPV Vaccine exactly 0% of White parents gave “My children are not sexually active and don’t need this vaccine” as their answer whereas 17% of Hispanics and African Americans and 26% of Asians gave this as the reason for not vaccinating.
These results remind us that human beings are complicated and that opinions vary by age, ethnicity and several other factors that we don’t have time to analyze here. One thing is certain, however, the measles, mumps and the human papilloma virus are equal-opportunity threats and the sooner we can get everyone on the same page to combat them the better.
Download our detailed report here: