Legal
Understanding Audience Engagement for the Paris 2024 Summer Olympics
Excitement is building for the Paris 2024 Summer Olympic Games as over 10,000 athletes from around the world prepare to showcase their incredible talents on this global stage. The City of Light will be teeming with fans and well-wishers who have traveled from near and far to watch and enjoy the Games. Those unable to attend can watch broadcasts on NBC and Telemundo, and networks like USA and the Golf Channel or stream the content on Peacock.
This year's Games are highly anticipated as they are the first full-capacity Olympics since the pandemic began. However, consumers’ media consumption habits changed significantly during the pandemic. To understand how audience engagement with the 2024 Summer Olympics might be impacted, ThinkNow conducted a quantitative research study among a nationally representative sample of U.S. adults.
Download the Audience Engagement: Paris 2024 Summer Olympic Games Report here.
Consumer Sentiment
The study revealed that a significant majority (68%) of U.S. adults plan to watch at least some of the Summer Olympics, marking a rise in enthusiasm compared to previous Games. This is particularly exciting considering fewer than half watched the 2022 Winter Olympics and 2020 Summer Olympics.
Asians (76%) expressed the most interest in watching this year’s Games, followed by African Americans (75%), Hispanics (74%) and non-Hispanic Whites (67%), demonstrating the growing diversity of U.S. viewers of this year’s Games.
Millennials (74%) are the largest generational cohort expressing interest in the Summer Olympic Games, followed by Gen X (71%) and Gen Z (68%). At 62%, Boomers show the least interest. That means that this year’s viewers will not only be more diverse but also skew younger, an important insight for brands looking to get in front of these influential groups.
Viewership
The study also uncovered distinct differences among various demographic groups in viewership patterns. Overall, 31% of viewers plan to watch the Olympics every day, with African Americans (30%) and non-Hispanic Whites (29%) close to the average, while Asians show less daily viewership at 16%. A significant portion of the audience plans to watch the Games on most days, with Asians leading at 52%, followed by African Americans (46%), Hispanics (49%), and non-Hispanic Whites (44%). Asians (25%) are more likely to view the Olympics only on days when their preferred sporting events are on, compared to 21% of non-Hispanic Whites and 18% of Hispanics.
Motivations and Preferences
Consumers plan to watch the games for various reasons, with the primary motivations being a love for their favorite sports, a sense of patriotism and a desire to gain cultural understanding. Gymnastics appeals to all groups, with Asians showing the highest interest at 52%. Basketball is particularly popular among African Americans, with 59% expressing interest. Swimming attracts a higher percentage of Asians (29%) and non-Hispanic Whites (27%), while Track and Field is favored by African Americans (38%).
Baseball sees notable interest among Hispanics (23%) and non-Hispanic Whites (23%) despite not appearing at the Olympic Games this year. The sport returns for the 2028 Summer Olympics in Los Angeles. Beach Volleyball is most popular among non-Hispanic Whites (26%), whereas Boxing finds more favor among Hispanics (25%). Soccer is especially popular among Hispanics, with 35% expressing interest, significantly higher than other groups. The study also revealed varied levels of enthusiasm and engagement among different demographic groups and generations. Overall, 45% of respondents completely agree that watching the U.S. compete in the Olympics fills them with pride. This sentiment is strongest among Hispanics (53%) and Baby Boomers (57%), while African Americans (40%) and Gen Z (35%) show less enthusiasm. The anticipation for the Olympics every four years is high, with 34% of the total market expressing strong agreement, particularly among Hispanics (43%) and Baby Boomers (47%). Thirty-nine percent of respondents view new sports like Surfing and Skateboarding favorably, with Millennials (47%) showing the most support and Boomers being the least enthusiastic (19%).
Learning about the culture of the host country is an appealing aspect for 43% of viewers, especially Gen Z (48%), although Asians (30%) and Boomers (26%) expressed less interest in diverse cultures. A significant portion of respondents, led by Hispanics (33%) and Millennials (35%), often go out of their way to watch their favorite Olympic events, with African Americans (17%) being less likely to do so.
The Olympics also serve as a family bonding occasion for 31% of viewers, particularly among Millennials (35%), though Boomers (20%) are less likely to share this view. A significant portion of respondents plan to share Olympic content on social media, with Gen Z (28%) being the most active and Boomers (9%) being the least.
Media Consumption
Finally, different demographic groups and generations show notable differences in media consumption habits. Non-Hispanic Whites (45%) and Baby Boomers (54%) are more likely to watch the Olympics on NBC/traditional network TV compared to Hispanics (28%) and Gen Z (23%). Online streaming platforms such as Peacock and NBC.com are particularly popular among Asians (42%) and Millennials (49%), indicating a preference for digital consumption among younger audiences. In contrast, cable/satellite options like CNBC, USA Network, and Telemundo are favored by Hispanics (33%) and, to a lesser extent, by Baby Boomers (26%).
A small percentage of viewers across all demographics are unsure about their viewing method, with Asians (6%) and Gen Z (7%) showing slightly higher uncertainty. These trends highlight the shift towards digital streaming among younger generations and the continued preference for traditional TV among older viewers.
Summer Olympics Key Takeaways
As technology continues to reshape how audiences engage with major events like the 2024 Summer Olympics, these findings underscore the importance for broadcasters and organizers to adapt their strategies to cater to consumers’ diverse viewing habits and preferences across different age groups.
Download the Audience Engagement: Paris 2024 Summer Olympic Games Report here.
we demistify diverse communities through research technology
Legal
The Growing Appeal of Asian Entertainment
Hollywood once dominated the domestic entertainment market, while foreign content had its niche in art houses and with ethnic broadcasters. That era has ended, and the fastest-growing entertainment segments are now coming from Asia. From Korean dramas (K-Dramas) to Bollywood, anime, and pop music, Asian entertainment is experiencing an unprecedented boom. But this didn’t happen overnight. This genre’s rise has been a steadily growing cultural force that, in the TikTok era, has captivated Americans of all ethnicities and backgrounds.
But what's fueling this phenomenon, and how is it changing how we consume media? To delve deeper into the increasing popularity of Asian entertainment among American audiences, ThinkNow tapped into our online market research panels and conducted a nationally representative quantitative survey of 2,000 adults, yielding intriguing findings.
Download the report here.
Consumer Habits
The internet, particularly the explosion of social media platforms, has been a catalyst for the proliferation of Asian media. These platforms offer a constant stream of bite-sized content that transcends language barriers. Compelling snippets of Korean Pop (K-Pop) dance routines, Japanese anime and Bollywood films have ignited curiosity among American audiences.
Japanese anime and Korean dramas are the most consumed content by 46% and 40% of Americans, respectively, followed closely by Chinese movies, Korean music and Bollywood movies. Gen Z is leading in consumption, with 62% consuming Japanese anime, followed by nearly 50% of Millennials who are also anime fans. In music, K-Pop reigns supreme, with 34% of Gen Z listening. Women, in particular, are driving the growth of both K-Pop and K-Dramas in the U.S. Their consumption of these two forms of entertainment surpasses male consumption by 10 percentage points each.
Asian Entertainment’s Appeal
So, what exactly is drawing audiences in? The answer lies in the unique appeal of Asian entertainment. For Asian Americans, the connection might be rooted in heritage or family ties, while others discover it through organic exploration on social media or through word-of-mouth recommendations. For the mainstream audience, the allure is multifaceted. They are attracted to the addictive nature of K-Dramas, with 53% stating that the storylines hook them.
Streaming Platforms
Accessing Asian entertainment is a challenge for some consumers. While streaming services have contributed to the diffusion of this content, 20% of consumers face difficulties accessing it, primarily due to limited availability on some streaming platforms. Netflix, however, remains the leading platform for video content, while Spotify and YouTube Music dominate the music scene. The survey reveals an emerging trend of viewers subscribing to multiple platforms to satisfy their Asian entertainment needs. A considerable portion of consumers expressed willingness to pay for a dedicated Asian content streaming service, particularly among Gen Z. As more platforms add Asian content, its consumption will likely increase among other key demographics.
Viewership Trends
Plot and storylines are the primary drivers of viewership, followed by genre and recommendations. However, the most significant takeaway is the overwhelmingly positive perception of Asian entertainment's influence on the broader market. Viewers across various ethnicities and age groups reported a sense of cultural connection and appreciation for the positive values often portrayed.
The Takeaway
As Asian entertainment continues to expand its global reach and influence, it is becoming increasingly clear that it’s not a passing trend. Music groups like Korea’s BTS and BLACKPINK, and series like Squid Game and anime/manga/games from Japan like Dragon Ball, Pokémon and Naruto as well as popular content from China, India, The Philippines and Malaysia promote cross-cultural understanding and are poised to create a lasting legacy of positivity within the media landscape. The future of Asian entertainment looks bright, with content poised to continue captivating American audiences as its availability grows.
Download your free copy of the report here.
we demistify diverse communities through research technology
Legal
The Pulse of American Voters: Insights from the 2024 Presidential Election Survey
Americans are gearing up to make their voices heard as the 2024 Presidential Election approaches. With only six months before ballots are cast, emotions are running high as the nation prepares for one of the most consequential elections in history. ThinkNow tapped into the pulse of likely voters with a nationwide online quantitative survey, uncovering the attitudes and trends shaping this pivotal moment in American democracy.
Download the report here.
A Diverse and Engaged Electorate
The survey, which reached 2,000 Americans and 1,443 likely voters, highlighted a significant level of engagement among various demographic groups. While approximately 80% of Non-Hispanic Whites, Asians, and African Americans expressed their intention to vote, around 70% of Hispanics indicated the same. Despite historical patterns suggesting a potential gap between reported intentions and actual turnout, the demographic differences align closely with past trends.
Not everyone, however, is interested in voting. Among the top explanations cited was the lack of appealing candidates, with Gen Zers exhibiting the lowest interest in politics overall. Furthermore, Baby Boomers and Non-Hispanic Whites were most likely to express dissatisfaction with the current slate of candidates.
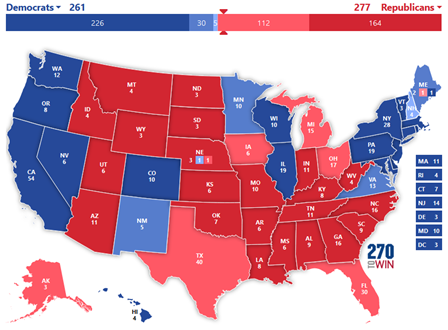
Seven States Poised to Determine Election Outcome
One of the survey's most notable findings was the even split among likely voters between Republican and Democratic candidates. In pivotal swing states such as Arizona, Georgia, North Carolina, and Michigan, Republican candidates held a clear edge, potentially tipping the scales in favor of the GOP. If actual voting results were to match current survey results, the Republican party would obtain the 270 electoral votes needed to win the White House.
Interestingly, if Michigan, with its 15 electoral votes, were to vote for the Democrats, they would retain the White House.
TV News Still Rules
When it comes to sourcing information about candidates, traditional media outlets such as TV news and news websites remain the primary channels for likely voters. However, social media and conversations with family and friends also play a significant role, particularly among younger demographics and certain ethnic groups.
Interestingly, the choice of information sources varied across swing states, reflecting each region's diverse media landscapes and campaigning strategies.
The Economy Takes Center Stage
Amidst a myriad of issues, the economy emerged as the foremost concern for likely voters nationwide. Healthcare, social security, and immigration also ranked prominently among voters' priorities, highlighting the multifaceted nature of electoral decision-making. Notably, Republican and Democratic voters exhibited divergent priorities, with the economy, immigration, and a strong military resonating strongly among the former, while healthcare and gun laws were top issues for the latter.
Furthermore, generational disparities on issues were evident, with Millennials prioritizing anti-poverty initiatives and LGBTQ+ rights. Gen Xers and Boomers, on the other hand, focused more on traditional concerns like abortion and national security. Gen Z cares more about student loan repayment than other groups by a wide margin. In swing states, variations in issue salience were observed, reflecting each region's unique socio-political landscapes and demographic compositions and the need to target messaging at the local level.
Challenges to Electoral Confidence
Despite the impending electoral showdown, concerns lingered regarding the fairness and integrity of the electoral process. Alarmingly, less than half of likely voters expressed confidence in the upcoming elections' fairness, with Republican voters exhibiting the highest levels of skepticism. Surprisingly, a substantial proportion of Hispanics voiced doubts about the election's fairness, underscoring the need for enhanced efforts to bolster confidence and transparency in the electoral system.
In Conclusion
As the 2024 Presidential Election approaches, the insights gleaned from ThinkNow's survey offer a snapshot of the diverse perspectives and priorities shaping the American electorate as they currently exist. Public opinion will certainly shift in the coming months, but these findings can provide valuable guidance for candidates, policymakers, and stakeholders navigating the intricacies of current American electorate. Ultimately, democracy is founded on the principles of participation and representation. With an evenly divided electorate, the outcome of the coming election will be determined by the enthusiasm each party can generate.
Download the report here.
we demistify diverse communities through research technology
Legal
American Families Approach 2024 with Cautious Optimism
Financial curveballs sent many American families reeling in 2023. Household budgets were squeezed by rising interest rates, surging prices on everyday goods, and a stagnating housing market. Consumers were feeling strapped. That sentiment, however, appears to be waning. The question is, to what extent?
To take the pulse of consumers’ feelings about their financial well-being ahead of a highly anticipated election, ThinkNow conducted a nationally representative quantitative survey. The survey highlights consumers’ hopes and anxieties as we move into 2024. Let's unpack the key findings to gain insights about where we stand.
Download the report here.
Optimism Is on the Rise
Nearly twice as many respondents in our survey anticipate an improvement in their financial situation (both personal and family) for 2024 (38%) compared to those expecting a decline (20%) when compared to 2023. And, around two-thirds of respondents feel confident managing their finances moving into 2024. African Americans and Baby Boomers lead in this category, while Gen Z lags behind. This gap highlights a potential need for targeted financial education initiatives, especially among younger consumers.
Some Still Feeling Overwhelmed
The financial optimism isn't shared equally. Hispanics, non-Hispanic Whites, and Millennials top the list of those feeling financially overwhelmed. While N.H. Whites worry about retirement more than African Americans, both groups face significant pressure. Interestingly, Baby Boomers seem the most grounded, with the lowest reported stress.
Compared to last year, almost half of the respondents have reported a significant increase in their financial anxiety—notably, women, N.H. Whites and Gen Xers are at the forefront of this trend. Despite these challenges, optimism isn’t lost. Approximately two-thirds of respondents believe their finances will improve in 2024, with Gen Z and Millennials emerging as the most optimistic.
Navigating the Debt Dilemma
Debt looms large, with half of the respondents burdened by it. While Asians and Gen Z carry less debt, Millennials and Gen X grapple with debt, especially credit card debt, the most. Making payments is a struggle for many, with African Americans, Gen Z, and women the most impacted. Rising interest rates add another layer of anxiety, particularly for African Americans and Baby Boomers. Previously sustainable debt levels can become overwhelming as interest rates rise.
As per the headlines, inflation is the top financial concern across the board, followed by unexpected expenses and housing costs. Gen Z worries less about inflation and the economy compared to older generations, but housing affordability and saving for the future weigh heavily on their minds.
Fortunately, over half of respondents actively seek support when stressed about finances, especially Gen Z and Millennials, known for being more open and vocal about their lives. While most respondents are likely to reach out to family and friends for advice, the willingness to openly talk about finances is still somewhat taboo. African Americans and Baby Boomers are ‘very uncomfortable’ talking about their finances with others.
Promoting Financial Wellness
Finally, the survey emphasizes the importance of financial education, with an overwhelming majority acknowledging its crucial role in financial well-being. This underscores the need for financial literacy programs accessible across all demographics to empower individuals to manage their finances confidently.
Remember This
America's financial landscape is diverse, with different groups facing unique challenges and holding varying degrees of hope. Recognizing these disparities and fostering financial literacy across all generations and ethnic groups is key to building a more financially secure and resilient economy.
For deeper insights into the ThinkNow 2024 Consumer Financial Wellness Report, download it here for free.
we demistify diverse communities through research technology
Legal
Unwrapping the Top Five Multicultural Holiday Shopping Trends in 2023
The 2023 holiday shopping season kicked off strong, with Adobe Analytics reporting a record $9.8 billion in Black Friday online sales, up 7.5% from 2022.Cyber Monday numbers were even stronger, with consumers spending $12.4 billion, a 9.6% increase over last year. So, what does this mean for December sales and the rest of the holiday shopping season? ThinkNow recently conducted a nationally representative quantitative survey of 1,500 consumers revealing insights into what Americans buy and spend for the holidays. From shopping habits to spending patterns, let's delve into the top five trends shaping the 2023 holiday shopping season.
Download the report here.
Top Holiday Shopping Trends
- Pre-Holiday Shopping: According to the survey, 2 out of 5 consumers preferred to kick-start their holiday shopping before Black Friday with many aiming to beat the holiday rush and avoid potential price increases and last-minute shipping delays. These early birds plan to strategically spread their purchases over the entire holiday season to help reduce feelings of overwhelm and keep the budget.
- Spending Sentiments: The robust start to the holiday shopping season may not last. Dollar sales growth is projected to slow from 6% last year to 3.3% this year, according to S&P Global Market Intelligence. Our survey corroborates this trend and shows that:
- Planned gift spending is waning: This year's average planned expenditure on gifts is $433, a noteworthy dip from $506 in 2018.
- Gift-giving opt-outs are rising: Nearly 20% of respondents are opting out of gift-giving altogether this season.
- Interest-free loans are gaining traction: 30% of respondents plan to leverage interest-free installment loan services like Pay in 4, AfterPay or Klarna.
- Spheres of Influence: Multicultural consumers rely heavily on their social circles for holiday gift ideas. When shopping for holiday gifts, family and friends remain the top source of inspiration for consumers, followed by in-store displays, with Hispanic consumers particularly receptive to the latter.
- Digital-First Shopping: More than half of consumers plan to make holiday purchases online this year, with e-commerce giants like Amazon, eBay, and Temu leading the way. Most online purchases will be made via smartphones, highlighting the growing role of mobile devices in the shopping experience. Asian consumers are most likely to shop online, while Millennials are most likely to use mobile apps.
- Top Gift Categories: Clothing, gift cards, and toys/games emerge as the frontrunners in this year's holiday gift categories. Gift cards are most popular with Baby Boomers, while Millennials are most likely to buy a voice-controlled product like Google Home or Amazon Alexa.
Implications for Businesses
The changing consumer landscape presents challenges and opportunities during the holiday season. Our findings suggest that businesses should focus on the following strategies to engage multicultural consumers during this time to build goodwill that could spill over to other peak spending seasons:
- Embrace cultural nuances. Multicultural consumers are a growing and influential segment of the U.S. population, and spending habits differ by ethnicity. For example, 41% of Asian consumers planned to start their shopping on Black Friday compared to the 27% Total Market Average. Over 40% of Hispanics (most commonly foreign-born and Spanish-dominant) plan to celebrate Three Kings' Day on January 6, extending the holiday shopping season into the new year. This presents a unique opportunity to engage these consumers with targeted campaigns and promotions.
- Prioritize e-commerce and omnichannel experiences. Online shopping soared during the COVID-19 pandemic and has continued to grow, but consumers are also enjoying the ability to gather in person again. Businesses must optimize their e-commerce platforms and mobile app experiences to cater to the growing mobile-first consumer base while offering seamless integration between online and offline experiences, like in-store pickup.
- Offer competitive prices and promotions. Inflation woes and government shutdown rumors have made consumers more price-sensitive – they are actively seeking deals and discounts. Use data-driven insights to tailor offers and discounts to specific cultural groups based on their preferences. Offer flexible payment solutions like installments or buy-now-pay-later options to cater to various financial situations.
- Provide exceptional customer service. Good customer service is always important, but it is especially critical during the stress of the holiday season. Train employees on cultural sensitivity and offer multilingual customer service options to make it easy for customers to communicate in their preferred language. Most importantly, respond promptly to inquiries and concerns and demonstrate empathy and understanding.
Conclusion
The 2023 holiday shopping season is starting strong, with several key trends emerging. Early birds are taking advantage of extra discounts and promotions, while spending sentiments are mixed due to economic uncertainties. Online shopping continues to dominate the landscape, with over half of consumers planning to purchase online. This presents a unique opportunity for businesses catering to multicultural consumers who are expected to drive significant growth during the holiday season.
Download the full report here for a deep dive into the findings and more cultural insights.
we demistify diverse communities through research technology
Legal
How Race, Age and Gender Shape Attitudes Towards Mental Health
Mental health has been in the news quite a bit lately. Dozens of U.S. states are currently suing Meta for contributing to the youth mental health crisis by inserting addictive features into their products, while the U.S. Surgeon General is touring the nation to bring awareness to the growing epidemic of loneliness and isolation. The country has endured periods of low national morale, such as in the 1970s when high inflation and the energy crisis worsened public sentiment following the Vietnam War. The current mood, however, feels different. Gallup recently reported that national mental health is at an all-time low, with few bright spots to lift spirits.
To better understand how Americans are feeling and their attitudes towards mental health in general, ThinkNow conducted a nationally representative quantitative survey of 1,500 respondents and found some interesting differences among ethnic, age and gender groups.
Download the report here.
Technology
For example, 52% agree that technology and social media have a negative impact on mental health, but when broken out by race, 61% of Whites felt technology had a negative effect, and only 48% of Hispanics thought it did.
While technology has helped us keep in touch with friends and family in faraway places, it appears to have degraded our ability to connect in person. Staying connected online is a double-edged sword since the same news feed that brings us pictures of the grandkids and fluffy kittens also feeds us news about the wars in Israel and Ukraine, the dysfunction in Washington, the latest mass shooting and the climate crisis.
Hispanics may have a built-in defense against the isolation technology breeds, owing to their large, multigenerational households, strong social support systems, and tendency to use social media to stay connected with relatives abroad.
Age and Gender
When asked how individuals rate their mental health, men rate it higher than women by 11 percentage points, and Baby Boomers rank it highest at 83%, saying it’s good or excellent vs. 57% of Gen Z saying the same.
Gen Z spends the most amount of time on social media, so the notion that social media negatively affects mental health appears to be correlated. Unfortunately, Gen Z is also the generation that’s least comfortable discussing mental health concerns with healthcare professionals. Only 40% of them state they’re comfortable discussing their issues with a professional compared to 60% of Millennials and 65% of Boomers.
Race Affects Attitudes
As seen in previous research conducted by ThinkNow, Asian Americans lag other groups when it comes to awareness of mental health issues. Twenty-four percent of Asian Americans believe that having a mental health issue is a sign of weakness compared to the 16% average for all groups. Asians are also considerably less likely to be aware of mental health services in their communities (42% vs. 55%) and most likely to seek out information on social media (51% vs. 35%).
Black Americans, however, are the most likely to engage in self-help (68% vs 58% on average) and more likely to be aware of resources. Black women, in particular, are good role models when it comes to mental health awareness. According to The Black Consumer Project, 63% of Black women believe that mental health is an essential part of overall health compared to 50% of non-Blacks.
The Role of Medication
Opinions on the role medication plays in the treatment of mental health vary considerably by age. When asked whether medication is the best treatment for mental health issues, the most significant difference we saw was the split between Millennials where 40% think medication is the best treatment, and Boomers, where only 13% believe medication is best.
We also saw differences by race with Asians being the least likely to think medication was best (20% vs. 30% for non-Hispanic Whites) and gender, with men being more likely than women to believe in medication (13% vs 8%). Thirty-two percent of men, however, think you can “snap out of” mental health problems vs. only 20% of women who agree. Men are more likely than women to believe that most mental health problems can be easily fixed (37% vs 22%), so their higher support for medicine may be masking other attitudes.
What’s next for mental health in America?
America faces diverse and interconnected mental health challenges influenced by technology, age, ethnicity and external factors. Understanding these differences can help when developing messaging and services that reach individuals most in need of assistance. While our society is starting to normalize talking about mental health, we still lack supportive environments and services are often difficult to access. Technology like social media can harm our mental health if not managed, but technological innovations like telemedicine and wellness apps can guide and support us in improving our outlook. A holistic and inclusive approach with open dialogue, support systems, and awareness is vital in navigating towards a healthier, more mentally resilient society.
we demistify diverse communities through research technology
Legal
Inclusive Beauty: Navigating Consumer Diversity and Shifting Preferences
The beauty industry has transformed in recent years driven by consumer demands for products that align with their cultural values and personal beliefs. While the top cosmetic brands continue to be L’Oreal and Estee Lauder, they are being challenged by younger, edgier brands like Selena Gomez’s Rare Beauty, Rihanna’s Fenty and e.l.f. Cosmetics. Consumer opinion, however, is not homogeneous. There are significant differences in preferences based on ethnicity, age, income and gender. ThinkNow uncovered some of those differences in our recent Inclusive Beauty Report based on a nationally representative online survey of 2,800 respondents.
Download the full results of the survey here.
The Rise of Conscious Consumerism
The era of conscious consumerism has brought about a major shift in the beauty industry. Increasingly, consumers seek products that align with their values, whether minimizing harm to animals, supporting sustainable practices, or promoting inclusivity. This has led to a growing demand for cosmetics and beauty products that are cruelty-free, meaning they are not tested on animals and that are considered inclusive.
Interestingly, while nearly half of cosmetic consumers want cruelty-free brands, 88% of them are still not cruelty-free. However, the fastest growing brands like e.l.f. and Rare Beauty are both cruelty-free and vegan. Legacy companies that want to compete in today’s market are being pushed to adopt these practices in their formulations and testing processes.
Cultural Insights and Multicultural Consumer Preferences
While the market as-a-whole is trending towards conscious consumerism, there are significant multicultural differences. For example, the demand for all-vegan cosmetics appears to be driven by non-Hispanic White consumers.
Additionally, since non-Hispanic Whites are, on average, ten years older than multicultural Americans, 42% of them choose brands based on how they address age-related needs vs. 30% of Hispanics who value age-related needs. Asians value products that offer solutions for different skin tones (37%) vs products that are endorsed by celebrities (15%) while Black and non-Hispanic White consumers are more likely to value brands that have a variety of price points. Understanding and addressing these specific preferences, as supported by cultural consumer insights, is crucial for building a loyal customer base.
Age and Income Drive Preferences
One might assume that younger consumers would be most interested in conscious consumerism. Gen Z however, is much less likely to seek out vegan cosmetic brands (19%) than Millennials (33%) or Gen X (31%). Gen X is more likely to seek out organic/natural ingredients (41%) than the 36% average for other age groups.
Income, however, is one of the factors that most affect cosmetic product preferences. For example, those earning more than $80K a year are significantly more likely to choose brands that are cruelty-free (53%) and vegan (42%) than those earning less than $40K annually (39%) and 21%), respectively. This insight-driven approach doesn't just enhance product offerings; it also builds trust and loyalty among diverse consumer groups.
The Impact of Inclusive Beauty
The beauty industry's shift towards cruelty-free, vegan, and inclusive beauty products aligns with trends observed in multicultural consumer insights. Younger generations are the most statistically diverse in history and wield the power to affect change. They are communicating their expectations to brands or starting their own and challenging heteronormative stereotypes of “beauty.” Companies willing to adapt to these culture shifts will stay relevant as consumer tastes change and contribute to a more compassionate and diverse world.